Agile Protein Interactomes DataServer
APID (Agile Protein Interactomes DataServer) is a new full redesigned version of APID (previous resource published in Nucleic Acids Research 2006, 34 Web Server issue: W298-W302) that provides a comprehensive collection of protein interactomes for more than 400 organisms based in the integration of known experimentally validated protein-protein physical interactions (PPIs). Construction of the interactomes is done with a methodological approach to report quality levels and coverage over the proteomes for each organism included. In this way, APID provides interactomes from specific organisms that in 25 cases have more than 500 proteins. As a whole APID includes a comprehensive compendium of 90,379 distinct proteins and 678,441 singular interactions.
The analytical and integrative effort done in APID unifies PPIs from primary databases of molecular interactions (BIND, BioGRID, DIP, HPRD, IntAct, MINT) and also from experimentally resolved 3D structures (PDB) where more than two distinct proteins have been identified. In this way, 8,388 structures have been analyzed to find specific protein-protein interactions reported with details of their molecular interfaces. APID also includes a new data visualization web-tool that allows the construction of sub-interactomes using query lists of proteins of interest and the visual exploration of the corresponding networks, including an interactive selection of the properties of the interactions (i.e. the reliability of the "edges" in the network) and an interactive mapping of the functional environment of the proteins (i.e. the functional annotations of the "nodes" in the network).
APID :: REFERENCE
When using APID data, we would like you to provide REFERENCE to our work quoting the following publications:
- Alonso-L�pez D, Campos-Laborie FJ, Guti�rrez MA, Lambourne L, Calderwood MA, Vidal M, De Las Rivas J. APID database: redefining protein-protein interaction experimental evidences and binary interactomes. Database (Oxford). 2019; doi: 10.1093/database/baz005. [ Full Text | PDF | PMID: 30715274 ]
- Alonso-L�pez D, Guti�rrez MA, Lopes KP, Prieto C, Santamaria R, De Las Rivas J. APID interactomes: providing proteome-based interactomes with controlled quality for multiple species and derived networks. Nucleic Acids Research 2016; doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw363. [ Full Text | PDF | PMID: 27131791 ]
Related publications:
- Prieto C, De Las Rivas J. APID: Agile Protein Interaction DataAnalyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34(Web Server issue):W298-302. [Full Text | PDF | PMID: 16845013 ]
- Hernandez-Toro J, Prieto C, De Las Rivas J. APID2NET: unified interactome graphic analyzer. Bioinformatics. 2007 Sep 15;23(18):2495-7. [Full Text | PDF | PMID: 17644818 ]
APID :: LICENSE
 APID Interactomes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
APID Interactomes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
APID :: MAIN PAGE
Search for the INTERACTOME of E. Coli at a given quality level and download it in your computer as a tabulated text file clicking on [ Get selected INTERACTOME] button.
APID :: SEARCH FOR ONE PROTEIN
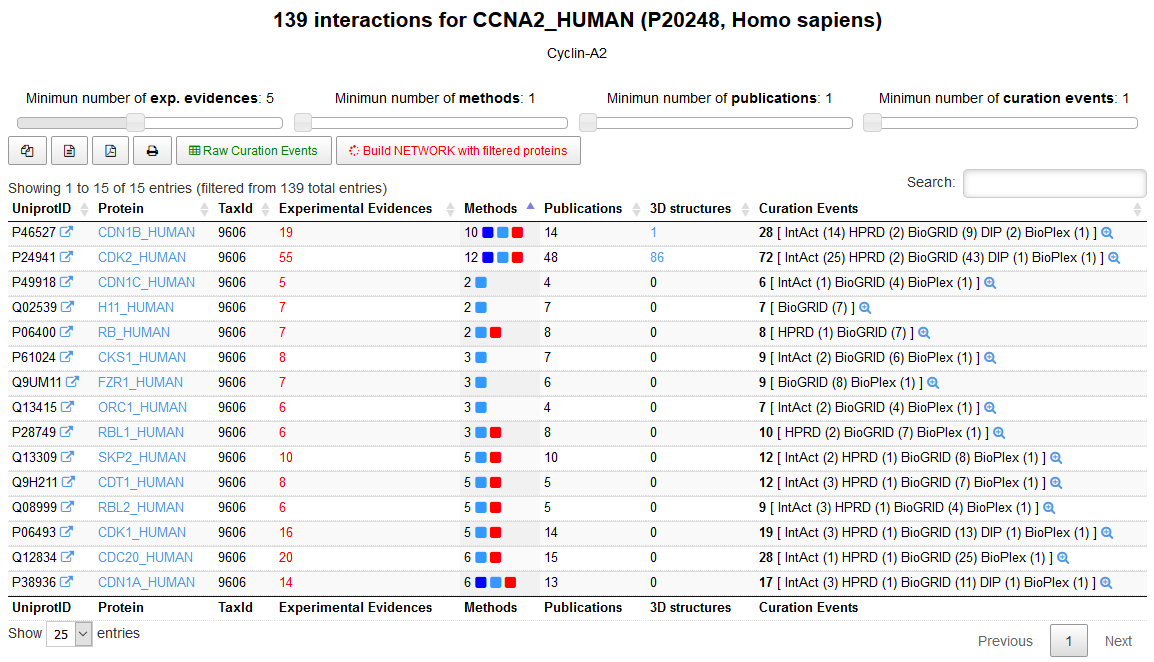
Search for the interactions of a protein (Cyclin A2, CCNA2_HUMAN) using menu [ Search: One protein ]. Once the protein is found, apply some quality filters corresponding to a minimum number of experimental evidences that prove the interactions (e.g. ≥5) and a minimum number of publications that report the interactions (e.g. ≥2). In this way more reliable interactions can be selected.
Explore the curation events for each interaction using the magnifying glass icon [ ].
APID :: BUILD THE INTERACTOME FOR A LIST OF PROTEINS :: STEP 1
Prepare a list of proteins using Uniprot Name identifiers (e.g. "RASK_HUMAN") or ENTREZ Gene Symbol identifiers (e.g. "KRAS") and place it in the menu [ Search: List of proteins ]. Once all the proteins are found, the list will be presented on a new window, as it is shown below, and all of them can be selected to build a network.
APID :: BUILD THE INTERACTOME FOR A LIST OF PROTEINS :: STEP 2
Build a protein interaction NETWORK with the selected proteins and explore it with the new APID network visualization web-tool that allows interactive selection of the properties of the interactions (i.e. the reliability of each edge) and interactive color mapping of the functional environment of the proteins. The view below corresponds to the network build using "List1" (i.e. the first one of the lists of proteins provided as examples at [ Search: List of proteins ]). This list has 33 human proteins that are included in the known human NOTCH signaling pathway (this canonical pathway can be seen at: http://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?hsa04330).
The network can be exported as a figure (.JPG or .PNG) and as a file (.TXT)
APID :: INTERACTION NETWORK THAT REVEALS PROTEIN COMPLEXES
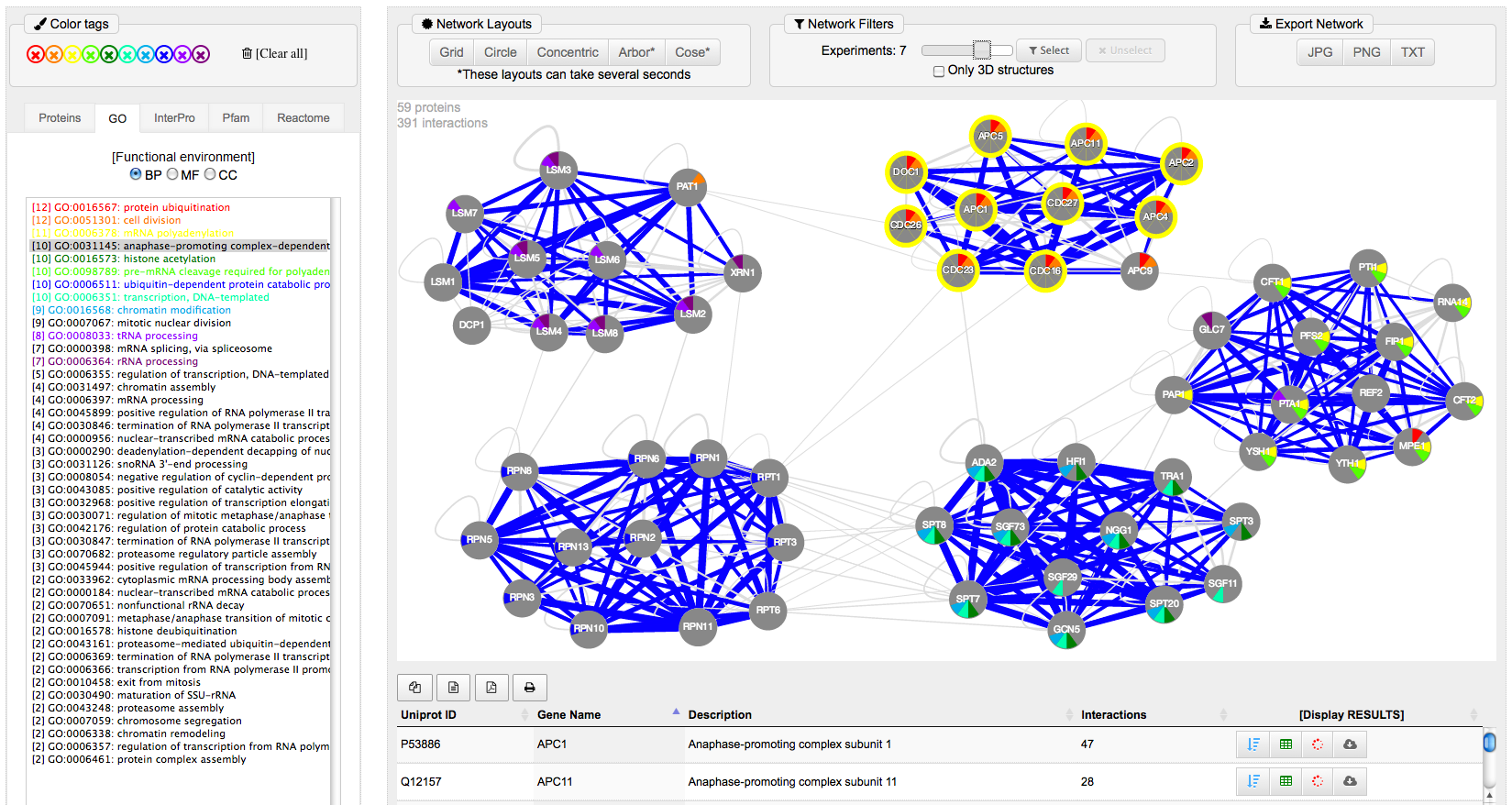
In this example we search with "List2" (second example in the menu [ Search: List of proteins ]). This list includes a collection of 59 proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae involved in different nuclear DNA and RNA processes. Once selected these proteins, we applied the Build NETWORK menu button and go to the visualization web-tool selecting "Arbor" in "Network layout" and "2 Experiments" in "Network filters". In this way, a network with 59 nodes and 391 edges is showed, revealing the clear presence of 5 distinct protein complexes. The figures show the network also using the selection of functions marked with different colors and, in the panel below, the selection of the just interactions that are proven by 3D structural data.
APID :: BUILD A PROTEIN COMPLEX WITH ITS STRUCTURAL INTERACTORS
In this example we search with "List3" (third example in the menu [ Search: List of proteins ]). This list includes the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase σ70 holoenzyme, a protein complex composed of 5 subunits that has its 3D structure determined (e.g. PDB: 4JK1, 4JK2), plus other 15 proteins that are known to interact with this complex. The figure below shows the view of such proteins with the selection in blue of just the protein interactions derived from 3D structures. The proteins are colored according to their functional annotations derived from GO BP (Gene Ontology Biological Process).
APID server was built with a protein and proteome-centered strategy, using UniProt database (http://www.uniprot.org) as the main guide to identify and handle all the proteins and to map them into the reference proteomes of each species (based on the new proteomes resource that UniProt has recently developed: http://www.uniprot.org/proteomes/). In this way UniProt (including both Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL) was used as the main reference database and we used protein or gene identifier recursive mapping to UniProtKB AC/ID as the key way to integrate and unify data, thus avoiding duplications or incorrect identifications. To provide a global view of the methodology and procedures followed to build APID, a graphic scheme (see figure below) presents the main workflow with the pipelines and steps applied to integrate the protein-protein interaction data.
- APID version: March 2021
- APID version: January 2019 (Full app update)
- APID version: March 2018
- APID version: June 2017
- APID version: June 2016
- APID version: January 2016
APID :: BRIEF STATISTICS
APID version: March 2021
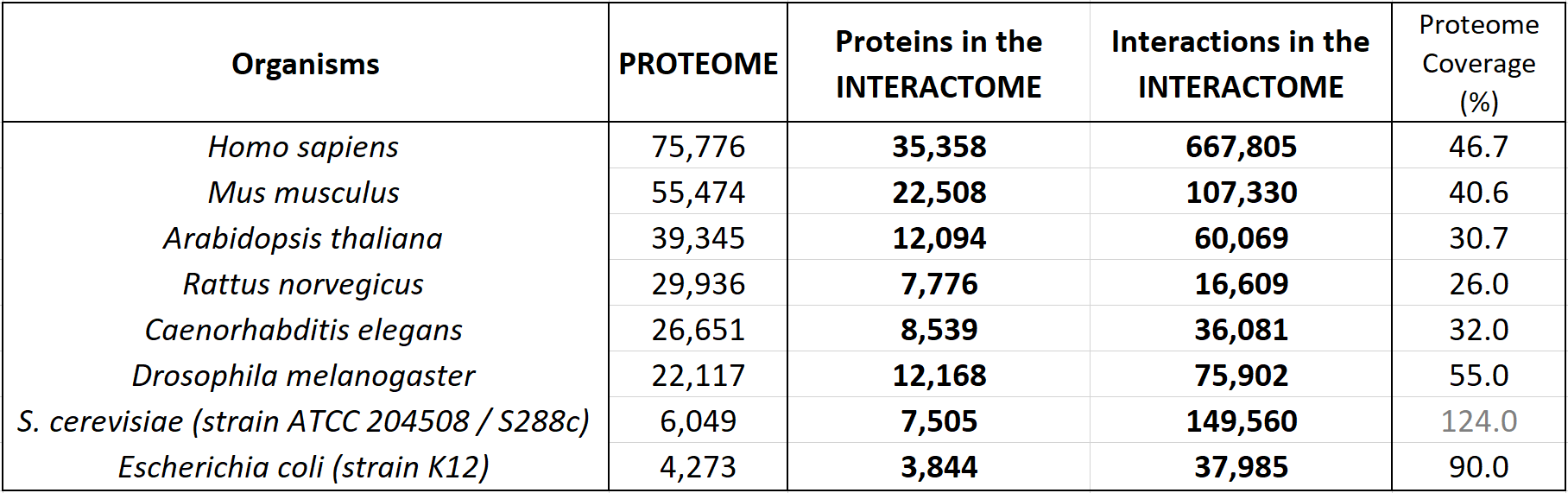
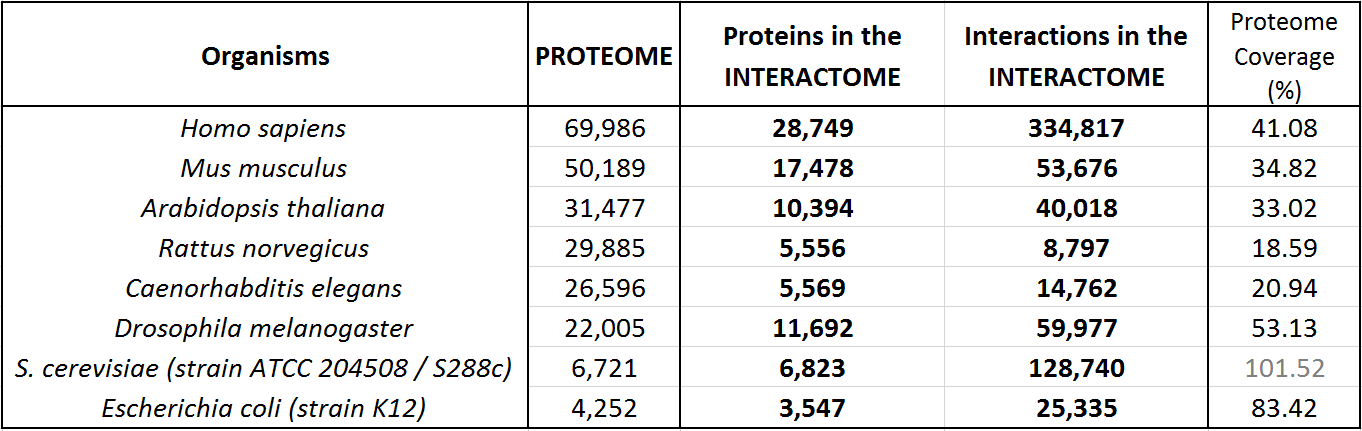
The following table shows an update of the statistics about the interactomes for several well known organisms. These data indicate the coverage over the whole proteomes (as reported by UniProt Reference Proteomes, that include both Swiss-Prot reviewed proteins and TrEMBL unreviewed proteins for each organism).
APID :: VERSIONS OF THE DATABASES USED
APID version: March 2021
Interaction Databases versions:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| IntAct | 18/12/2020 |
| HPRD | 12/04/2010 |
| BioGRID | Versi�n 4.2.193 |
| DIP | 05/02/2017 |
| BioPlex | Version 2.0 |
Protein and Proteome Reference Database version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| UniProt | UniProtKB (Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL) 2020_12 |
Protein 3D Structures Databases version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| PDB | 10-11-2015 |
| PDBsum | 10-11-2015 |
APID :: BRIEF STATISTICS
APID version: January 2019
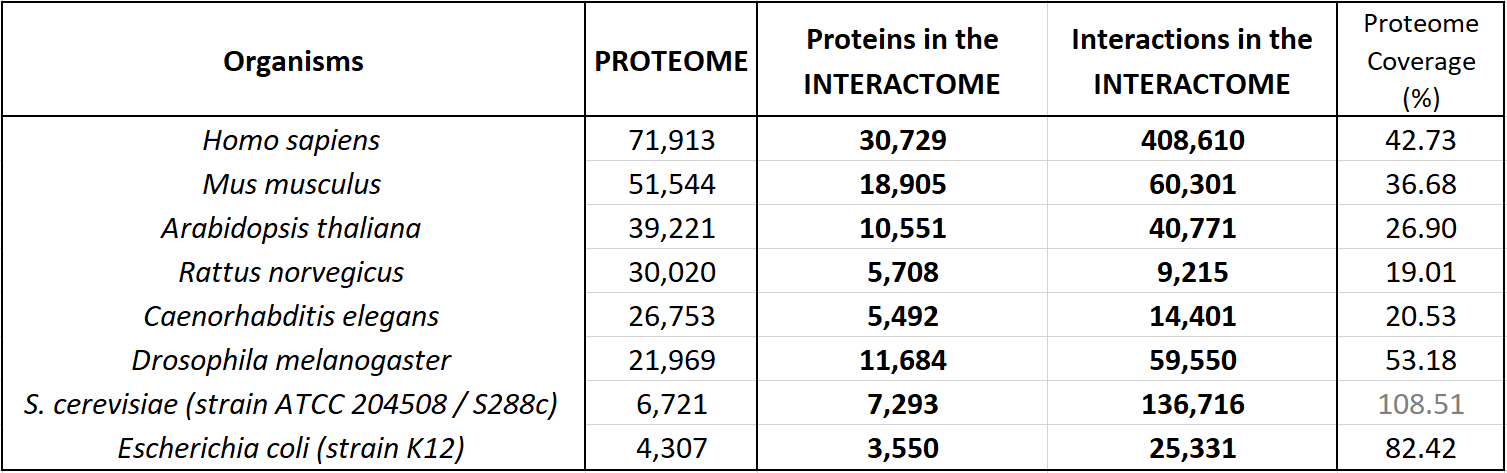
The following table shows an update of the statistics about the interactomes for several well known organisms. These data indicate the coverage over the whole proteomes (as reported by UniProt Reference Proteomes, that include both Swiss-Prot reviewed proteins and TrEMBL unreviewed proteins for each organism).
APID :: VERSIONS OF THE DATABASES USED
APID version: January 2019
Interaction Databases versions:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| IntAct | 07/09/2018 |
| HPRD | 12/04/2010 |
| BioGRID | Versi�n 3.4.164 (25/08/2018) |
| DIP | 05/02/2017 |
| BioPlex | Version 2.0 |
Protein and Proteome Reference Database version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| UniProt | UniProtKB (Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL) 2018_09 |
Protein 3D Structures Databases version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| PDB | 10-11-2015 |
| PDBsum | 10-11-2015 |
APID :: BRIEF STATISTICS
APID version: March 2018
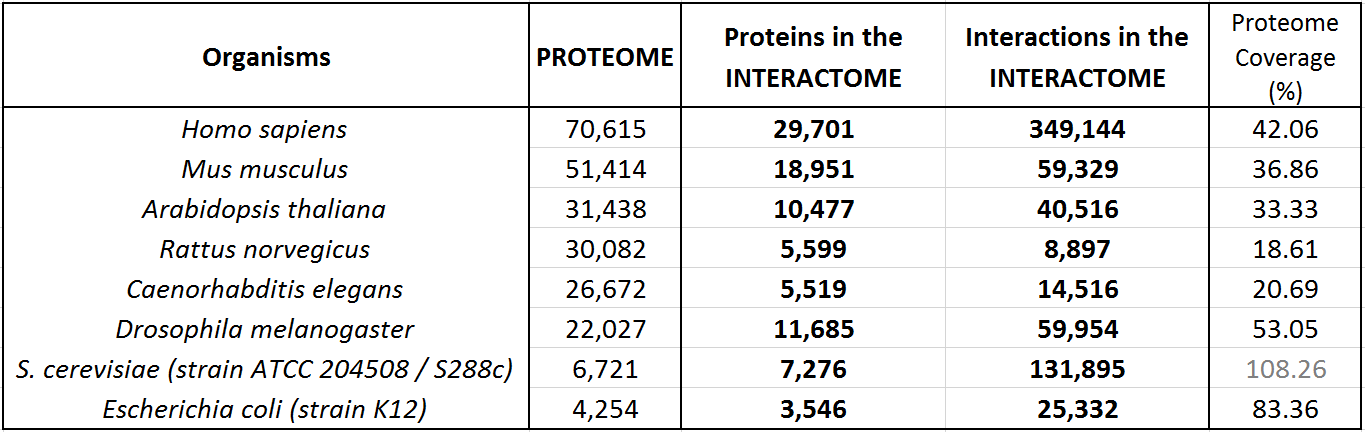
The following table shows an update of the statistics about the interactomes for several well known organisms. These data indicate the coverage over the whole proteomes (as reported by UniProt Reference Proteomes, that include both Swiss-Prot reviewed proteins and TrEMBL unreviewed proteins for each organism).
APID :: VERSIONS OF THE DATABASES USED
APID version: March 2018
Interaction Databases versions:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| IntAct | 27/01/2018 |
| HPRD | 12/04/2010 |
| BioGRID | Version 3.4.157 (25/01/2018) |
| DIP | 05/02/2017 |
| BioPlex | Version 2.0 |
Protein and Proteome Reference Database version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| UniProt | UniProtKB (Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL) 2018_01 |
Protein 3D Structures Databases version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| PDB | 10-11-2015 |
| PDBsum | 10-11-2015 |
APID :: BRIEF STATISTICS
APID version: June 2017
The following table shows an update of the statistics about the interactomes for several well known organisms. These data indicate the coverage over the whole proteomes (as reported by UniProt Reference Proteomes, that include both Swiss-Prot reviewed proteins and TrEMBL unreviewed proteins for each organism). In this way, for example, in the case of human (Homo sapiens) the current UniProt Reference Proteome includes only 20,201 reviewed proteins, but we prefer to map to the complete UniProt dataset because many reported experiments are done with proteins included in TrEMBL.
APID :: VERSIONS OF THE DATABASES USED
APID version: June 2017
Interaction Databases versions:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| IntAct | 09/04/2017 |
| HPRD | 12/04/2010 |
| BioGRID | Version 3.4.148 (25/04/2017) |
| DIP | 05/02/2017 |
| BioPlex | Version 2.0 (Unpublished) 01/06/2017 |
Protein and Proteome Reference Database version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| UniProt | UniProtKB (Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL) 2017_05 |
Protein 3D Structures Databases version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| PDB | 10-11-2015 |
| PDBsum | 10-11-2015 |
APID :: BRIEF STATISTICS
APID version: June 2016
The following table shows statistics about some of the largest interactomes included in the new APID. These data indicate a fair coverage over the whole proteomes. In the case of human (Homo sapiens), the number of proteins with reported interactions reaches a 40% of the human proteome. In the case of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), the number of proteins with reported interactions is larger than the UniProt proteome (http://www.uniprot.org/proteomes/UP000002311) because its interactome includes yeast putative proteins (coming from TrEMBL but not present in the UniProt reference proteome).
APID :: VERSIONS OF THE DATABASES USED
APID version: June 2016
Interaction Databases versions:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| IntAct | 20/06/2016 |
| HPRD | 12/04/2010 |
| BioGRID | Version 3.4.137 (25/05/2016) |
| DIP | 30/04/2016 |
| BioPlex | 06/12/2015 |
Protein and Proteome Reference Database version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| UniProt | UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot 2016_06 (08/06/2016) |
Protein 3D Structures Databases version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| PDB | 10-11-2015 |
| PDBsum | 10-11-2015 |
APID :: BRIEF STATISTICS
APID version: January 2016
The following table shows statistics about some of the largest interactomes included in the new APID. These data indicate a fair coverage over the whole proteomes. In the case of human (Homo sapiens), the number of proteins with reported interactions reaches a 40% of the human proteome. In the case of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), the number of proteins with reported interactions is larger than the UniProt proteome (http://www.uniprot.org/proteomes/UP000002311) because its interactome includes yeast putative proteins (coming from TrEMBL but not present in the UniProt reference proteome).
APID :: VERSIONS OF THE DATABASES USED
APID version: January 2016
Interaction Databases versions:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| IntAct | 26/12/2015 |
| HPRD | 12/04/2010 |
| BioGRID | Version 3.4.132 (01/01/2016) |
| DIP | 29/10/2015 |
| BioPlex | 06/12/2015 |
Protein and Proteome Reference Database version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| UniProt | UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot 2016_01 (20/01/2016) |
Protein 3D Structures Databases version:
| Database | Version |
|---|---|
| PDB | 10-11-2015 |
| PDBsum | 10-11-2015 |
APID :: REFERENCE
When using APID data, we would like you to provide REFERENCE to our work quoting the following publications:
- Alonso-L�pez D, Campos-Laborie FJ, Guti�rrez MA, Lambourne L, Calderwood MA, Vidal M, De Las Rivas J. APID database: redefining protein-protein interaction experimental evidences and binary interactomes. Database (Oxford). 2019; doi: 10.1093/database/baz005. [ Full Text | PDF | PMID: 30715274 ]
- Alonso-L�pez D, Guti�rrez MA, Lopes KP, Prieto C, Santamaria R, De Las Rivas J. APID interactomes: providing proteome-based interactomes with controlled quality for multiple species and derived networks. Nucleic Acids Research 2016; doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw363. [ Full Text | PDF | PMID: 27131791 ]
Related publications:
- Hernandez-Toro J, Prieto C, De Las Rivas J. APID2NET: unified interactome graphic analyzer. Bioinformatics. 2007 Sep 15;23(18):2495-7. [Full Text | PDF | PMID: 17644818 ]
- Prieto C, De Las Rivas J. APID: Agile Protein Interaction DataAnalyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34(Web Server issue):W298-302. [Full Text | PDF | PMID: 16845013 ]
APID :: LICENSE
 APID Interactomes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
APID Interactomes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
APID :: ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS TO SOURCES DATABASES and TECHNOLOGIES
Interaction Databases
Protein and Proteome Reference Database
Protein 3D Structures Databases
Annotation Databases
Standards Initiatives
Technologies
APID :: FUNDING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Funding has been provided to Dr. J. De Las Rivas group by the Local Government, "Junta de Castilla y Leon" (JCyL, Valladolid, Spain, grants number BIO/SA68/13) and the Spanish Government, "Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad" (MINECO, ISCiii, Madrid, Spain, grants number PI12/00624, PI15/00328 and AC14/00024).


![Figure 4: Build the interactome for a list of proteins [Step 1].](./APID_Figures/Fig4.png)
![Figure 5: Build the interactome for a list of proteins [Step 2].](./APID_Figures/Fig5_v1_NotchPathway.png)
![Figure 6: Build the interactome for a list of proteins [Step 2]. Exported network.](./APID_Figures/Fig6_v2_NotchPathway.jpg)